OOP
What is Object Oriented Programming?
Object-Oriented Programming (OOPs) is a type of programming that is based on objects rather than just functions and procedures. Individual objects are grouped into classes. OOPs implements real-world entities like inheritance, polymorphism, hiding, etc into programming. It also allows binding data and code together.
Why use OOPs?
- OOPs allows clarity in programming thereby allowing simplicity in solving complex problems
- Code can be reused through inheritance thereby reducing redundancy
- Data and code are bound together by encapsulation
- OOPs allows data hiding, therefore, private data is kept confidential
- Problems can be divided into different parts making it simple to solve
- The concept of polymorphism gives flexibility to the program by allowing the entities to have multiple forms
Main features of OOP:
- Inheritance - Inheritance is a process where one class acquires the properties of another.
- Encapsulation - Encapsulation in Java is a mechanism of wrapping up the data and code together as a single unit. For example getters and setters.
- Polymorphism - Polymorphism is the ability of a variable, function or object to take multiple forms.
- Data Abstraction - Abstraction is the methodology of hiding the implementation details from the user and only providing the functionality to the users.
What are the limitations of OOPs?
- Usually not suitable for small problems
- Requires intensive testing
- Takes more time to solve the problem
- Requires proper planning
- The programmer should think of solving a problem in terms of objects
What is a class?
A class is simply a representation of a type of object. It is the blueprint/plan/template that describes the details of an object.
What is an Object?
An object is an instance of a class. It has its own state, behavior, and identity.
What is the main difference between a class and an object?
An object is an instance of a class. Objects hold multiple information, but classes don’t have any information. Definition of properties and functions can be done in class and can be used by the object.
A class can have sub-classes, while an object doesn’t have sub-objects.
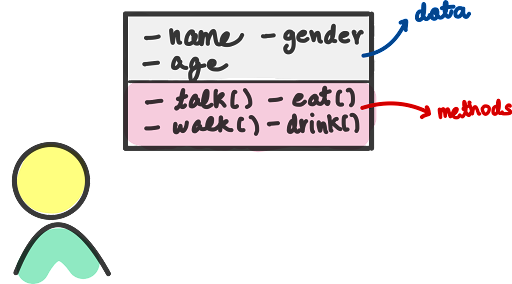
What is Encapsulation?
Encapsulation is an attribute of an object, and it contains all data which is hidden. That hidden data can be restricted to the members of that class.
Levels are Public, Protected, Private, Internal, and Protected Internal.
One can visualize Encapsulation as the method of putting everything that is required to do the job, inside a capsule and presenting that capsule to the user. What it means is that by Encapsulation, all the necessary data and methods are bind together and all the unnecessary details are hidden to the normal user. So Encapsulation is the process of binding data members and methods of a program together to do a specific job, without revealing unnecessary details.
Encapsulation can also be defined in two different ways:
- Data hiding:
Encapsulation is the process of hiding unwanted information, such as restricting access to any member of an object.
- Data binding:
Encapsulation is the process of binding the data members and the methods together as a whole, as a class
It’s a basic concept that most Java developers use without a lot of thought. In essence, it’s simply how you design a Java class. You bundle a set of attributes that store the current state of the object with a set of methods using these attributes.
What is an abstraction?
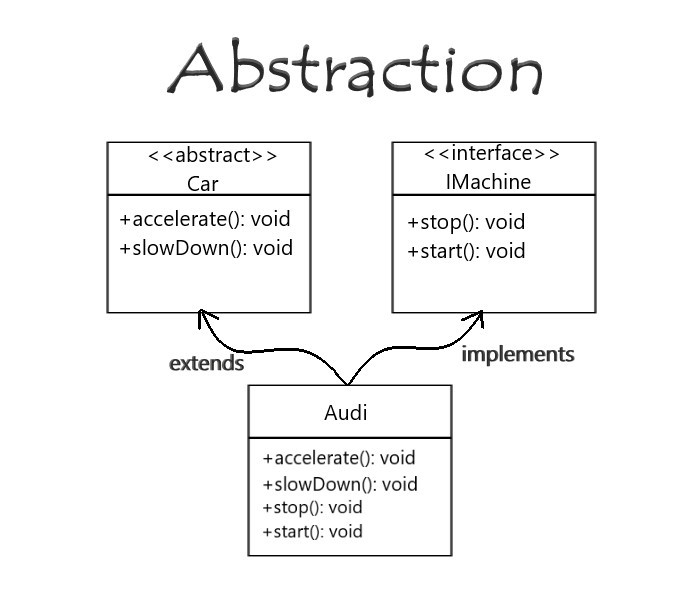
Abstraction is a useful feature of OOPS, and it shows only the necessary details to the client of an object. Meaning, it shows only required details for an object, not the inner constructors, of an object. Example – When you want to switch on the television, it is not necessary to know the inner circuitry/mechanism needed to switch on the TV. Whatever is required to switch on TV will be shown by using an abstract class.
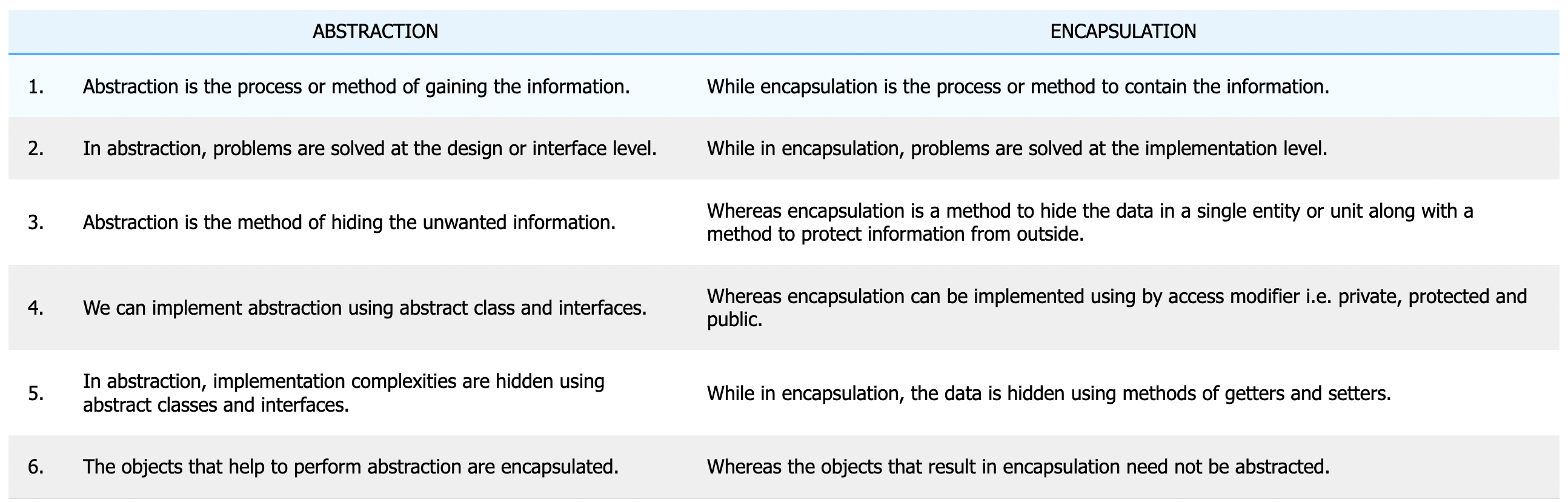
Difference between encapsulation and abstraction
Abstraction is the method of hiding the unwanted information. Whereas encapsulation is a method to hide the data in a single entity or unit along with a method to protect information from outside. We can implement abstraction using abstract class and interfaces.
Encapsulation: Information hiding
Abstraction: Implementation hiding
Encapsulation is to hide the variables or something inside a class, preventing unauthorized parties to use. So the public methods like getter and setter access it and the other classes call these methods for accessing
Abstraction involves the facility to define objects that represent abstract "actors" that can perform work, report on and change their state, and "communicate" with other objects in the system.
Consider the below real time example:
Encapsulation: As a driver you know how to start the car by pressing the start button and internal details of the starting operations are hidden from you. So the entire starting process is hidden from you otherwise we can tell starting operation is encapsulated from you.
OR
The driving wheel is encapsulated the process of rotating the wheel from you.
Abstraction:
Before mentioning anything about abstraction, we can take three different users here (I am calling them as entity)
1) You 2) Local Mechanic 3) Expert
You Entity: Since you know only to start the car by pressing a button and all other operations behind the scene are abstracted from you.
Local Mechanic Entity: Our local mechanic knows some of the implementation of starting the car, i.e. he can open car's bonnet and check the battery cable or chock etc. So in short Local Mechanic Entity knows some of the implementations of the car.
Expert Entity: Since our expert (Designer of the car) mechanic knows all the operations of our car, he can repair it very quickly. So in short Expert Entity knows all the implementations of the car.
The car's operation is completely abstracted from you and it is partially implemented to Local Mechanic Entity and fully implemented to Expert Entity. So you are an abstract class having only abstract methods, Local Mechanic Entity has extended You(Since he is also an ordinary user) and he implemented some of the methods and last our expert Entity extending Local Mechanic and implementing all the methods.
What is Polymorphism?
Polymorphism is composed of two words - “poly” which means “many”, and “morph” which means “shapes”. Therefore Polymorphism refers to something that has many shapes.
Polymorphism is nothing but assigning behavior or value in a subclass to something that was already declared in the main class. Simply, polymorphism takes more than one form.
In OOPs, Polymorphism refers to the process by which some code, data, method, or object behaves differently under different circumstances or contexts. Compile-time polymorphism and Run time polymorphism are the two types of polymorphisms in OOPs languages.
What is Inheritance?
Inheritance is a concept where one class shares the structure and behavior defined in another class. If Inheritance applied to one class is called Single Inheritance, and if it depends on multiple classes, then it is called multiple Inheritance.
What are manipulators?
Manipulators are the functions which can be used in conjunction with the insertion (<<) and extraction (>>) operators on an object. Examples are endl and setw.
Explain the term constructor
A constructor is a method used to initialize the state of an object, and it gets invoked at the time of object creation. Rules for constructor are:
- Constructor Name should be the same as a class name.
- A constructor must have no return type.
Define Destructor?
A destructor is a method which is automatically called when the object is made of scope or destroyed. Destructor name is also same as class name but with the tilde symbol before the name.
What is an Inline function?
An inline function is a technique used by the compilers and instructs to insert complete body of the function wherever that function is used in the program source code.
What is a virtual function?
A virtual function is a member function of a class, and its functionality can be overridden in its derived class. This function can be implemented by using a keyword called virtual, and it can be given during function declaration.
A virtual function can be declared using a token(virtual) in C++. It can be achieved in C/Python Language by using function pointers or pointers to function.
In Java, all non-static methods are by default "virtual functions." Only methods marked with the keyword final, which cannot be overridden, along with private methods, which are not inherited, are non-virtual.
What is a pure virtual function?
A pure virtual function is a function which can be overridden in the derived class but cannot be defined. A virtual function can be declared as Pure by using the operator =0.
Example –
Virtual void function1() // Virtual, Not pure
Virtual void function2() = 0 //Pure virtual
What does the keyword virtual represented in the method definition?
It means we can override the method.
What is a friend function?
A friend function is a friend of a class that is allowed to access to Public, private, or protected data in that same class. If the function is defined outside the class cannot access such information.
A friend can be declared anywhere in the class declaration, and it cannot be affected by access control keywords like private, public, or protected.
The designers of Java explicitly rejected the idea of friend as it works in C++. You put your "friends" in the same package. Private, protected, and packaged security is enforced as part of the language design.
James Gosling wanted Java to be C++ without the mistakes. I believe he felt that friend was a mistake because it violates OOP principles. Packages provide a reasonable way to organize components without being too purist about OOP.
NR pointed out that you could cheat using reflection, but even that only works if you aren't using the SecurityManager. If you turn on Java standard security, you won't be able to cheat with reflection unless you write security policy to specifically allow it.
https://stackoverflow.com/a/18634125/7931798
What is function overloading?
Function overloading is a regular function, but it is assigned with multiple parameters. It allows the creation of several methods with the same name which differ from each other by the type of input and output of the function.
Example
void add(int a, int b);
void add(double a, double b);
void add(Long a, Long b);
What is operator overloading?
Operator overloading is a function where different operators are applied and depends on the arguments. Operator,-,* can be used to pass through the function, and it has its own precedence to execute
Java doesn't supports operator overloading because it's just a choice made by its creators who wanted to keep the language more simple.
What is an abstract class?
An abstract class is a class which cannot be instantiated. Creation of an object is not possible with an abstract class, but it can be inherited. Java allows abstract and non-abstract methods in abstract class. A Java abstract class can have instance methods that implement a default behaviour.
You can't instantiate your abstract class, however you can instantiate a concrete subclass of your abstract class
An abstract class can implement an interface without implementing any of its methods.
What is a ternary operator?
The ternary operator is said to be an operator which takes three arguments. Arguments and results are of different data types, and it depends on the function. The ternary operator is also called a conditional operator.
variable = Expression ? this : that;
What is the use of finalize method?
Finalize method helps to perform cleanup operations on the resources which are not currently used. Finalize method is protected, and it is accessible only through this class or by a derived class.
In Java it is called right before the object is garbage collected.
What are the different types of arguments?
A parameter is a variable used during the declaration of the function or subroutine, and arguments are passed to the function body, and it should match with the parameter defined. There are two types of Arguments.
- Call by Value – Value passed will get modified only inside the function, and it returns the same value whatever it is passed into the function.
- Call by Reference – Value passed will get modified in both inside and outside the functions and it returns the same or different value.
What is the super keyword?
The super keyword is used to invoke the overridden method, which overrides one of its superclass methods. This keyword allows to access overridden methods and also to access hidden members of the superclass.
It also forwards a call from a constructor, to a constructor in the superclass.
We cannot use super() and this() on the same constructor.
What is method overriding?
Method overriding is a feature that allows a subclass to provide the implementation of a method that overrides in the main class. It will override the implementation in the superclass by providing the same method name, same parameter, and same return type.
What is an interface?
An interface is a collection of an abstract method. If the class implements an interface, it thereby inherits all the abstract methods of an interface.
Java uses Interface to implement multiple inheritances.
What are tokens?
A compiler recognizes a token, and it cannot be broken down into component elements. Keywords, identifiers, constants, string literals, and operators are examples of tokens.
Even punctuation characters are also considered as tokens. Example: Brackets, Commas, Braces, and Parentheses.
What is the main difference between overloading and overriding?
Overloading is static Binding, whereas Overriding is dynamic Binding. Overloading is nothing but the same method with different arguments, and it may or may not return the equal value in the same class itself.
Overriding is the same method names with the same arguments and return types associated with the class and its child class.
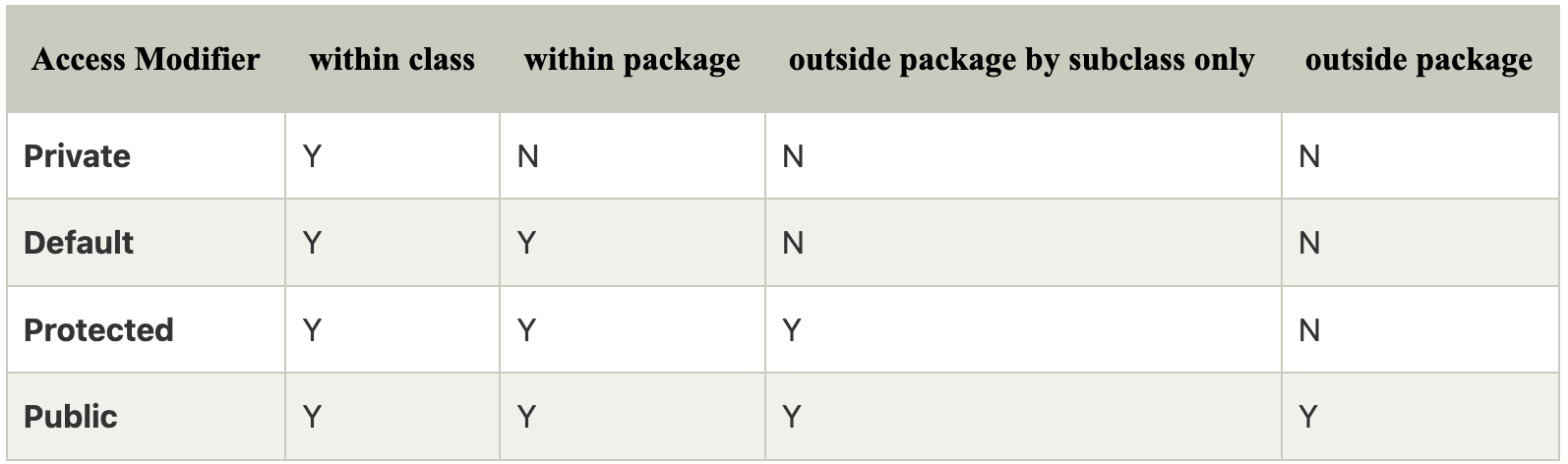
What are the access modifiers?
Access modifiers determine the scope of the method or variables that can be accessed from other various objects or classes. There are five types of access modifiers, and they are as follows:
Java has:
- Private
- Protected
- Public
- Default
Java doesn’t have:
- Friend
- Protected Friend
If a class has no modifier (the default, also known as package-private), it is visible only within its own package
What are access specifiers and what is their significance?
Access specifiers, as the name suggests, are a special type of keywords, which are used to control or specify the accessibility of entities like classes, methods, etc. Some of the access specifiers or access modifiers include “private”, “public”, etc. These access specifiers also play a very vital role in achieving Encapsulation - one of the major features of OOPs.
What are sealed modifiers?
Sealed modifiers are the access modifiers where the methods can not inherit it. Sealed modifiers can also be applied to properties, events, and methods. This modifier cannot be used to static members.
Java has it.
How can we call the base method without creating an instance?
Yes, it is possible to call the base method without creating an instance. And that method should be “Static method.”
Doing Inheritance from that class.
Use Base Keyword from a derived class.
What is the difference between new and override?
The new modifier instructs the compiler to use the new implementation instead of the base class function. Whereas, Override modifier helps to override the base class function.
What is dynamic or run time polymorphism?
Dynamic or Run time polymorphism is also known as method overriding in which call to an overridden function is resolved during run time, not at the compile time. It means having two or more methods with the same name, same signature but with different implementation.
What is Compile time Polymorphism and how is it different from Runtime Polymorphism?
Compile Time Polymorphism (Overloading):
Compile time polymorphism, also known as Static Polymorphism, refers to the type of Polymorphism that happens at compile time. What it means is that the compiler decides what shape or value has to be taken by the entity in the picture.
// In this program, we will see how multiple functions are created with the same name,
// but the compiler decides which function to call easily at the compile time itself.
class CompileTimePolymorphism{
// 1st method with name add
public int add(int x, int y){
return x+y;
}
// 2nd method with name add
public int add(int x, int y, int z){
return x+y+z;
}
// 3rd method with name add
public int add(double x, int y){
return (int)x+y;
}
// 4th method with name add
public int add(int x, double y){
return x+(int)y;
}
}
class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
CompileTimePolymorphism demo=new CompileTimePolymorphism();
// In the below statement, the Compiler looks at the argument types and decides to call method 1
System.out.println(demo.add(2,3));
// Similarly, in the below statement, the compiler calls method 2
System.out.println(demo.add(2,3,4));
// Similarly, in the below statement, the compiler calls method 4
System.out.println(demo.add(2,3.4));
// Similarly, in the below statement, the compiler calls method 3
System.out.println(demo.add(2.5,3));
}
}In the above example, there are four versions of add methods. The first method takes two parameters while the second one takes three. For the third and fourth methods, there is a change of order of parameters. The compiler looks at the method signature and decides which method to invoke for a particular method call at compile time.
Runtime Polymorphism (Overriding):
Runtime polymorphism, also known as Dynamic Polymorphism, refers to the type of Polymorphism that happens at the run time. What it means is it can't be decided by the compiler. Therefore what shape or value has to be taken depends upon the execution. Hence the name Runtime Polymorphism.
class AnyVehicle{
public void move(){
System.out.println(“Any vehicle should move!!”);
}
}
class Bike extends AnyVehicle{
public void move(){
System.out.println(“Bike can move too!!”);
}
}
class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
AnyVehicle vehicle = new Bike();
// In the above statement, as you can see, the object vehicle is of type AnyVehicle
// But the output of the below statement will be “Bike can move too!!”,
// because the actual implementation of object ‘vehicle’ is decided during runtime vehicle.move();
vehicle = new AnyVehicle();
// Now, the output of the below statement will be “Any vehicle should move!!”,
vehicle.move();
}
}As the method to call is determined at runtime, as shown in the above code, this is called runtime polymorphism.
What are the various types of constructors?
There are three types of constructors:
– Default Constructor – With no parameters.
– Parametric Constructor – With Parameters. Create a new instance of a class and also passing arguments simultaneously.
– Copy Constructor – Which creates a new object as a copy of an existing object.
Do we require a parameter for constructors?
No, we do not require a parameter for constructors.
What is a copy constructor?
This is a special constructor for creating a new object as a copy of an existing object. There will always be only one copy constructor that can be either defined by the user or the system.
A copy constructor in a Java class is a constructor that creates an object using another object of the same Java class.
That's helpful when we want to copy a complex object that has several fields, or when we want to make a deep copy of an existing object.
Like C++, Java also supports copy constructor. But, unlike C++, Java doesn’t create a default copy constructor if you don’t write your own.
What is early and late Binding?
Binding is nothing but the association of a name with the class. Static Binding is a binding in which name can be associated with the class during compilation time, and it is also called as early Binding.
Early binding refers to the assignment of values to variables during design time, whereas late Binding refers to the assignment of values to variables during run time.
Dynamic Binding is a binding in which name can be associated with the class during execution time, and it is also called as Late Binding.
Example of early binding:
public class NewClass {
public static class superclass {
static void print()
{
System.out.println("print in superclass.");
}
}
public static class subclass extends superclass {
static void print()
{
System.out.println("print in subclass.");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
superclass A = new superclass();
superclass B = new subclass();
A.print();
B.print();
}
}print in superclass.
print in superclass.
Example of late binding:
public class NewClass {
public static class superclass {
void print()
{
System.out.println("print in superclass.");
}
}
public static class subclass extends superclass {
@Override
void print()
{
System.out.println("print in subclass.");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
superclass A = new superclass();
superclass B = new subclass();
A.print();
B.print();
}
}print in superclass.
print in subclass.
What is ‘this’ pointer?
THIS pointer refers to the current object of a class. THIS keyword is used as a pointer which differentiates between the current object with the global object. It refers to the current object.
What is the difference between structure and a class?
The default access type of a Structure is public, but class access type is private. A structure is used for grouping data, whereas a class can be used for grouping data and methods. Structures are exclusively used for data, and it doesn’t require strict validation, but classes are used to encapsulate and inherent data, which requires strict validation.
What is the default access modifier in a class?
In Java, the default access modifier is package-private (Default) - visible only from the same package.
What are all the operators that cannot be overloaded?
Following are the operators that cannot be overloaded -.
- Scope Resolution (::)
- Member Selection (.)
- Member selection through a pointer to function (.*)
Java doesn't support operator overloading.
Whether static method can use no static members?
False.
What are a base class, subclass, and superclass?
The base class is the most generalised class, and it is said to be a root class.
A Subclass is a class that inherits from one or more base classes.
The superclass is the parent class from which another class inherits.
How many instances can be created for an abstract class?
Zero instances will be created for an abstract class. In other words, you cannot create an instance of an Abstract Class.
Can you create an instance of an abstract class?
No. Instances of an abstract class cannot be created because it does not have a complete implementation. However, instances of subclass inheriting the abstract class can be created.
Which OOPS concept is used as a reuse mechanism?
Inheritance is the OOPS concept that can be used as a reuse mechanism.
Which OOPS concept exposes only the necessary information to the calling functions?
Encapsulation
What are some other programming paradigms other than OOPs?
Programming paradigms refers to the method of classification of programming languages based on their features. There are mainly two types of Programming Paradigms:
- Imperative Programming Paradigm
- Declarative Programming Paradigm
Now, these paradigms can be further classified based:
1. Imperative Programming Paradigm: Imperative programming focuses on HOW to execute program logic and defines control flow as statements that change a program state. This can be further classified as:a) Procedural Programming Paradigm: Procedural programming specifies the steps a program must take to reach the desired state, usually read in order from top to bottom.b) Object-Oriented Programming or OOP: Object-oriented programming (OOP) organizes programs as objects, that contain some data and have some behavior.c) Parallel Programming: Parallel programming paradigm breaks a task into subtasks and focuses on executing them simultaneously at the same time.
2. Declarative Programming Paradigm: Declarative programming focuses on WHAT to execute and defines program logic, but not a detailed control flow. Declarative paradigm can be further classified into:a) Logical Programming Paradigm: Logical programming paradigm is based on formal logic, which refers to a set of sentences expressing facts and rules about how to solve a problemb) Functional Programming Paradigm: Functional programming is a programming paradigm where programs are constructed by applying and composing functions.c) Database Programming Paradigm: Database programming model is used to manage data and information structured as fields, records, and files.
How much memory does a class occupy?
Classes do not consume any memory. They are just a blueprint based on which objects are created. Now when objects are created, they actually initialize the class members and methods and therefore consume memory
Are there any limitations of Inheritance?
Yes, with more powers comes more complications. Inheritance is a very powerful feature in OOPs, but it has some limitations too. Inheritance needs more time to process, as it needs to navigate through multiple classes for its implementation. Also, the classes involved in Inheritance - the base class and the child class, are very tightly coupled together. So if one needs to make some changes, they might need to do nested changes in both classes. Inheritance might be complex for implementation, as well. So if not correctly implemented, this might lead to unexpected errors or incorrect outputs.
- Increases the time and effort required to execute a program as it requires jumping back and forth between different classes
- The parent class and the child class get tightly coupled
- Any modifications to the program would require changes both in the parent as well as the child class
- Needs careful implementation else would lead to incorrect results
What are the various types of inheritance?
The various types of inheritance include:
- Single inheritance
- Multiple inheritances
- Multi-level inheritance
- Hierarchical inheritance
- Hybrid inheritance
What is hybrid inheritance?
Hybrid inheritance is a combination of multiple and multi-level inheritance.
What is hierarchical inheritance?
Hierarchical inheritance refers to inheritance where one base class has more than one subclasses. For example, the vehicle class can have ‘car’, ‘bike’, etc as its subclasses.
What is the difference between multiple and multilevel inheritance?
Multiple Inheritance - Multiple inheritance comes into picture when a class inherits more than one base class. Example: A class defining a child inherits from two base classes Mother and Father
Multilevel Inheritance - Multilevel inheritance means a class inherits from another class which itself is a subclass of some other base class. Example: A class describing a sports car will inherit from a base class Car which in turn inherits another class Vehicle
How is data abstraction accomplished?
Data abstraction is accomplished with the help of abstract methods or abstract classes.
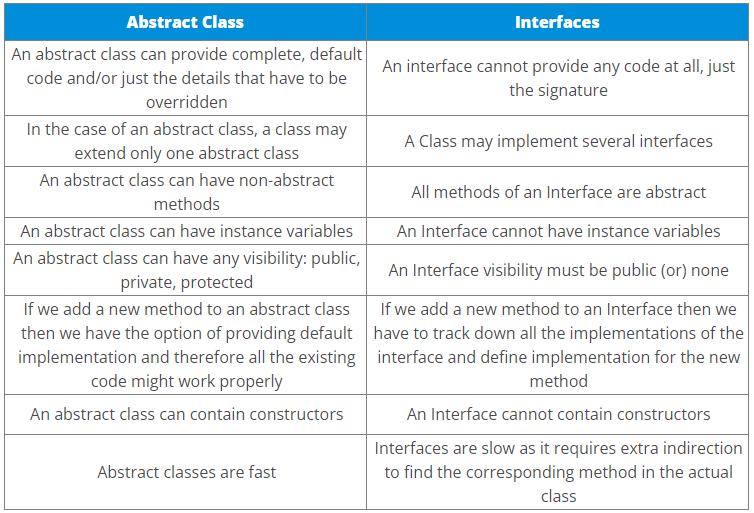
How is an abstract class different from an interface?
Interface and abstract class both are special types of classes that contain only the methods declaration and not their implementation. But the interface is entirely different from an abstract class. The main difference between the two is that, when an interface is implemented, the subclass must define all its methods and provide its implementation. Whereas when an abstract class is inherited, the subclass does not need to provide the definition of its abstract method, until and unless the subclass is using it.
Also, an abstract class can contain abstract methods as well as non-abstract methods.
ABSTRACT METHOD in Java, is a method that has just the method definition but does not contain implementation. A method without a body is known as an Abstract Method. It must be declared in an abstract class. The abstract method will never be final because the abstract class must implement all the abstract methods.
What is the difference between abstract classes and interfaces?
Can we run a Java application without implementing the OOPs concept?
Yes.
However, on the other hand, C++ can be implemented without OOPs, as it also supports the C-like structural programming model.
What will be the output of the below code?
class Scaler
{
static int i;
static
{
System.out.println(“a”);
i = 100;
}
}
public class Static Block
{
static
{
System.out.println(“b”);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println(“c”);
System.out.println(Scaler.i);
}
}Output:
b
c
a
100
Reason:
Firstly the static block inside the main-method calling class will be implemented. Hence ‘b’ will be printed first. Then the main method is called, and now the sequence is kept as expected.
What will be the output in below code?
public class Demo{
public static void main(String[] arr){
System.out.println(“Main1”);
}
public static void main(String arr){
System.out.println(“Main2”);
}
}Output:
Main1
Reason: Here the main() method is overloaded. But JVM only understands the main method which has a String[] argument in its definition. Hence Main1 is printed and the overloaded main method is ignored.
What is Garbage Collection(GC)?
GC is an implementation of automatic memory management. The Garbage collector frees up space occupied by objects that are no longer in existence.
What is a final variable?
A variable whose value does not change. It always refers to the same object by the property of non-transversity.
What is a try/ catch block?
A try/ catch block is used to handle exceptions. The try block defines a set of statements that may lead to an error. The catch block basically catches the exception.
What is a finally block?
A finally block consists of code that is used to execute important code such as closing a connection, etc. This block executes when the try block exits. It also makes sure that finally block executes even in case some unexpected exception is encountered.
What is an exception?
An exception can be considered as a special event, which is raised during the execution of a program at runtime, that brings the execution to a halt. The reason for the exception is mainly due to a position in the program, where the user wants to do something for which the program is not specified, like undesirable input.
What is exception handling?
An exception is an event that occurs during the execution of a program. Exceptions can be of any type – Runtime exception, Error exceptions. Those exceptions are adequately handled through exception handling mechanism like try, catch, and throw keywords.
What is the difference between an error and an exception?
Error - Errors are problems that should not be encountered by applications
Exception - Conditions that an application might try to catch
| Error | Exception | |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Classified as an unchecked type | Classified as checked and unchecked |
| Package | It belongs to java.lang.error | It belongs to java.lang.Exception |
| Recoverable/ Irrecoverable | It is irrecoverable | It is recoverable |
| It can't occur at compile time | It can occur at run time compile time both | |
| Example | OutOfMemoryError ,IOError | NullPointerException , SqlException |
Exceptions and errors both are subclasses of Throwable class. The error indicates a problem that mainly occurs due to the lack of system resources and our application should not catch these types of problems. Some of the examples of errors are system crash error and out of memory error. Errors mostly occur at runtime that's they belong to an unchecked type.
Exceptions are the problems which can occur at runtime and compile time. It mainly occurs in the code written by the developers. Exceptions are divided into two categories such as checked exceptions and unchecked exceptions.
Example of Error
public class ErrorExample {
public static void main(String[] args){
recursiveMethod(10)
}
public static void recursiveMethod(int i){
while(i!=0){
i=i+1;
recursiveMethod(i);
}
}
}
Output
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.StackOverflowError
at ErrorExample.ErrorExample(Main.java:42)
Example of Exception
public class ExceptionExample {
public static void main(String[] args){
int x = 100;
int y = 0;
int z = x / y;
}
}
Output
java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
at ExceptionExample.main(ExceptionExample.java:7)
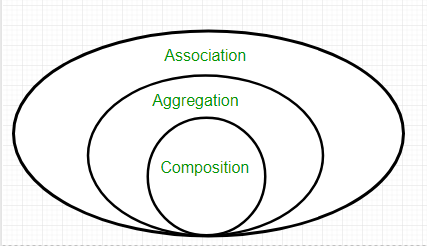
What is an association?
Association is a relationship where all object have their own lifecycle and there is no owner. Let’s take the example of Teacher and Student. Multiple students can associate with a single teacher and a single student can associate with multiple teachers but there is no ownership between the objects and both have their own lifecycle. These relationships can be one to one, one to many, many to one and many to many.
What do you mean by aggregation?
An aggregation is a specialised form of Association where all object has their own lifecycle but there is ownership and child object can not belong to another parent object. Let’s take an example of Department and teacher. A single teacher can not belong to multiple departments, but if we delete the department teacher object will not destroy.
It is a special form of Association where:
- It represents Has-A’s relationship.
- It is a unidirectional association i.e. a one-way relationship. For example, a department can have students but vice versa is not possible and thus unidirectional in nature.
- In Aggregation, both the entries can survive individually which means ending one entity will not affect the other entity.
What is composition in Java?
Composition is again a specialised form of Aggregation and we can call this as a “death” relationship. It is a strong type of Aggregation. Child object does not have their lifecycle and if parent object deletes all child object will also be deleted. Let’s take again an example of a relationship between House and rooms. House can contain multiple rooms there is no independent life of room and any room can not belongs to two different houses if we delete the house room will automatically delete.
Composition is a restricted form of Aggregation in which two entities are highly dependent on each other.
- It represents part-of relationship.
- In composition, both entities are dependent on each other.
- When there is a composition between two entities, the composed object cannot exist without the other entity.
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/association-composition-aggregation-java/
What is a marker interface?
A marker interface is an interface that has no methods or constants inside it. It provides run-time type information about objects, so the compiler and JVM have additional information about the object.
A marker interface is also called a tagging interface.
Though marker interfaces are still in use, they very likely point to a code smell and should be used carefully. The main reason for this is that they blur the lines about what an interface represents since markers don't define any behavior. Newer development favors annotations to solve some of the same problems.